Electric Furnace Transformers: Types, Applications & Structural Features | ZTelec China
11-17 2025 | By:
Electric furnace transformers are specifically designed to supply power for various industrial furnaces. They are categorized into three main types based on application scenarios: resistance furnace transformers, arc furnace transformers, and induction furnace transformers. These transformers play a critical role in mechanical part heating, heat treatment, metallurgical sintering, non-ferrous metal smelting, and salt bath furnace operations. Due to the extremely low initial resistance of heating elements or significant resistance changes during the heating process, electric furnace transformers are essential to reduce and regulate the input voltage between the furnace and the power grid.
1. Resistance Furnace Transformers
Resistance furnace transformers are widely used in mechanical part heating, heat treatment, powder metallurgy sintering, non-ferrous metal smelting, resistance heating furnaces, and salt bath furnaces.
- Core Function: Compensate for the excessively low initial resistance of heating elements or large resistance fluctuations during operation by adjusting and lowering the furnace’s input voltage.
- Cooling & Structural Designs:
- Small-capacity, low-voltage models (for small resistance furnaces and salt bath furnaces) are mostly dry-type transformers with enclosures, adopting natural cooling.
- Medium-capacity models use oil-immersed self-cooling technology.
- Large-capacity units rely on forced oil circulation water cooling for efficient heat dissipation.
2. Arc Furnace Transformers
Arc furnace transformers are specialized for steelmaking electric arc furnaces, featuring large capacity, complex structures, and high technical requirements.
- Key Specifications:
- Secondary voltage ranges from tens to hundreds of volts, requiring a wide adjustment range.
- Secondary current typically reaches several thousand to tens of thousands of amperes.
- Performance Requirements:
- Overload capacity: Must withstand 20% overload for 2 hours to meet high-power demands during the smelting cycle.
- Short-circuit resistance: Furnace charge collapse is common during steelmaking, leading to frequent short circuits. The primary side must be connected to a current-limiting reactor or have high impedance to restrict short-circuit current.
- Voltage Regulation Methods: Two primary approaches are used to adjust voltage for furnace operation (specific methods vary by equipment design).
3. Induction Furnace Transformers
Induction furnace transformers power induction furnaces for smelting ferrous and non-ferrous metals, and are classified into core-type and coreless-type designs.
- Core-Type Induction Furnaces: Function as transformers with an iron core and a short-circuited secondary winding. The primary winding connects to the power grid, while the secondary winding consists of just one turn (the metal bath). When current flows through the primary winding, an induced current circulates in the secondary winding (metal bath), generating heat to melt the metal.
- Coreless-Type Induction Furnaces: Rely on electromagnetic induction without an iron core, suitable for specialized smelting scenarios requiring high temperature uniformity.
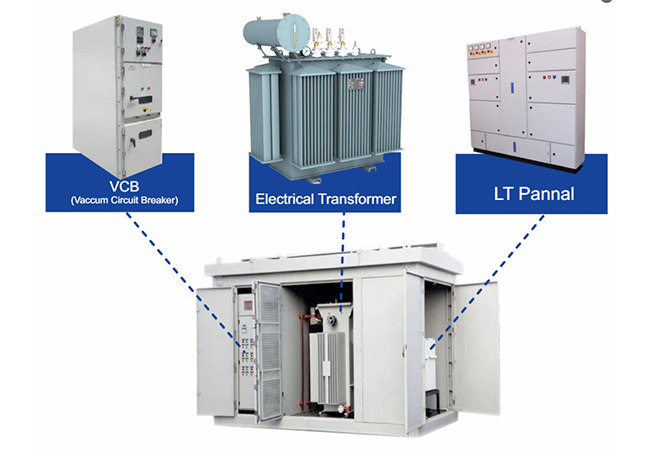
4. Structural Features of Electric Furnace Transformers
Electric furnace transformers integrate advanced design and manufacturing technologies to ensure reliability and performance:
- Iron Core: Made of high-quality oriented silicon steel sheets, processed by automatic cutting lines. Adopts 45° full miter joints, punch-free design, and non-woven glass tape binding to minimize loss and noise.
- Windings: Utilize the latest international primary and longitudinal insulation structures. Winding structure and insulation materials are carefully selected to ensure excellent mechanical strength.
- Core Advantages: Strong short-circuit resistance, high overload capacity, high efficiency, low energy loss, and safe, reliable operation.
- Capacity & Voltage Regulation:
- Capacity is configured based on arc furnace size and smelting processes.
- Voltage regulation options: On-load voltage regulation (for large furnaces, no series reactor required) and off-load voltage regulation (for small to medium furnaces, with or without series reactors).
- Impedance adjustment: High-voltage winding impedance can be modified at two voltage levels—either by switching series reactors on/off or changing the transformer’s internal connection method.
Why Choose ZTelec China’s Electric Furnace Transformers?
ZTelec China specializes in manufacturing custom electric furnace transformers tailored to industrial smelting and heating needs. Our products comply with international standards (IEC, IEEE, GB) and feature durable structures, efficient performance, and flexible customization. Whether for resistance, arc, or induction furnaces, we deliver reliable power solutions to enhance production efficiency and reduce energy consumption.
Contact our technical team today for a personalized quote or detailed technical consultation!
You may also find these interesting: